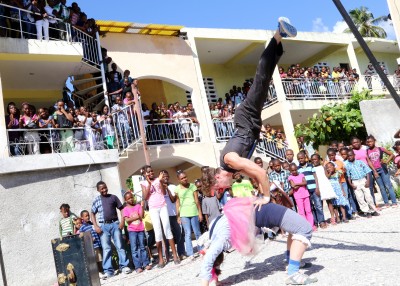
Need Your Daily Exercise? Try Clowning.
By Guest Blogger and Performer, Molly Siskin
There is no exhaustion like the one that comes at the end of a long day hard at work in clown training. Clowning has a particular way of exercising performers both physically and emotionally because in many ways it is both an art and sport.
You might not immediately think of clowns at athletes, but traditionally circus clowns would often perform alongside the acrobats in the troupe, executing some of the same skills but with a unique twist that only a clown can bring. Clowning is a very physical form of theatre and requires a high level of physical dexterity, awareness, and control. Additionally, the long hours and fast-paced schedule of a clowning career (particularly in the circus), require stamina and strength. Modern clown training is easily comparable to physical theatre or modern dance, both practices that utilize body movement to tell a story or convey a mood, and may even use similar exercises, games, and movement-improvisational work. The parallels between clown and dance have not gone unnoticed. Charlie Chaplin was once called “the greatest ballet dancer that ever lived” when he received his honorary Oscar. The ability to communicate a story with one’s body requires nuanced control of your body and facial muscles. Physical awareness and expressiveness take time, sweat, and practice. For some, that can mean a rigorous regiment of daily training to gain strength and physical ability. Famous Russian ballet dancer, Mikhail Baryshnikov once said, “Get used to pain. It’s part of a dancer’s life.”
One way that clowning differs from most dance is what Clown Theorist Jacques LeCoq called “the flop” or the moment the clown fails. If the clown is attempting an acrobatic stunt or a beautifully executed dance move, the flop often constitutes a fall or intentional use of incorrect form to complete an intricate or dangerous physical task. Falling and failing are fundamental parts of clowning, and although they appear to be chaos, they are approached very carefully. Just as in the principles of stage combat or stunt work, when falling, it is important to be in total control before you can safely appear to be out of control. Falling can take practice and time to perfect. A long day of falling is sure to leave a clown-in-training tired and sporting a new bruise or two.
In an era of more subtle, theatrical clowning gaining in prominence, not all clown routines are equally physically performative and taxing. However, clowning also takes a high level of emotional energy. Many teachers continue to develop LeCoq’s clown theories of finding each performer’s personal clown, following creative impulse, and staying strongly connected to an audience using the partial mask of a clown nose to both hide and reveal the performer who wears it. This methodology can leave the performer feeling very personally vulnerable, meanwhile staying connected to the audience can be both exhilarating and overwhelming. Many training programs emphasize honesty in clowning. Even when the clowning experience is not traumatic, being a proxy for a whole audience and honestly, openly, and physically expressing one’s experience can be exhausting.
At the end of a long day, a clown-in-training may feel like they have run a marathon, fallen off a chair, and attended a particularly moving therapy session. Though this may be exhausting, the feeling of using your whole body and emotional range, particularly when it is working towards the goal of laughter and joy, is particularly satisfying.
It is the personal satisfaction, sense of accomplishment, and cathartic release of emotion that are hallmarks of the workshops facilitated by Clowns Without Borders performers. Whether you are attending a workshop like “Find Your Funny” at the Omega Institute in New York, or are a refugee living in a refugee camp for the indefinite long-term, the workshop principles remain the same. People are encouraged to learn new physical skills. They are encouraged to build community with others through simple moments of joy that build into exuberant laughter. It’s like remembering a great secret you once forgot: That people can and do stay connected when bonds are formed in laughter.